Projects
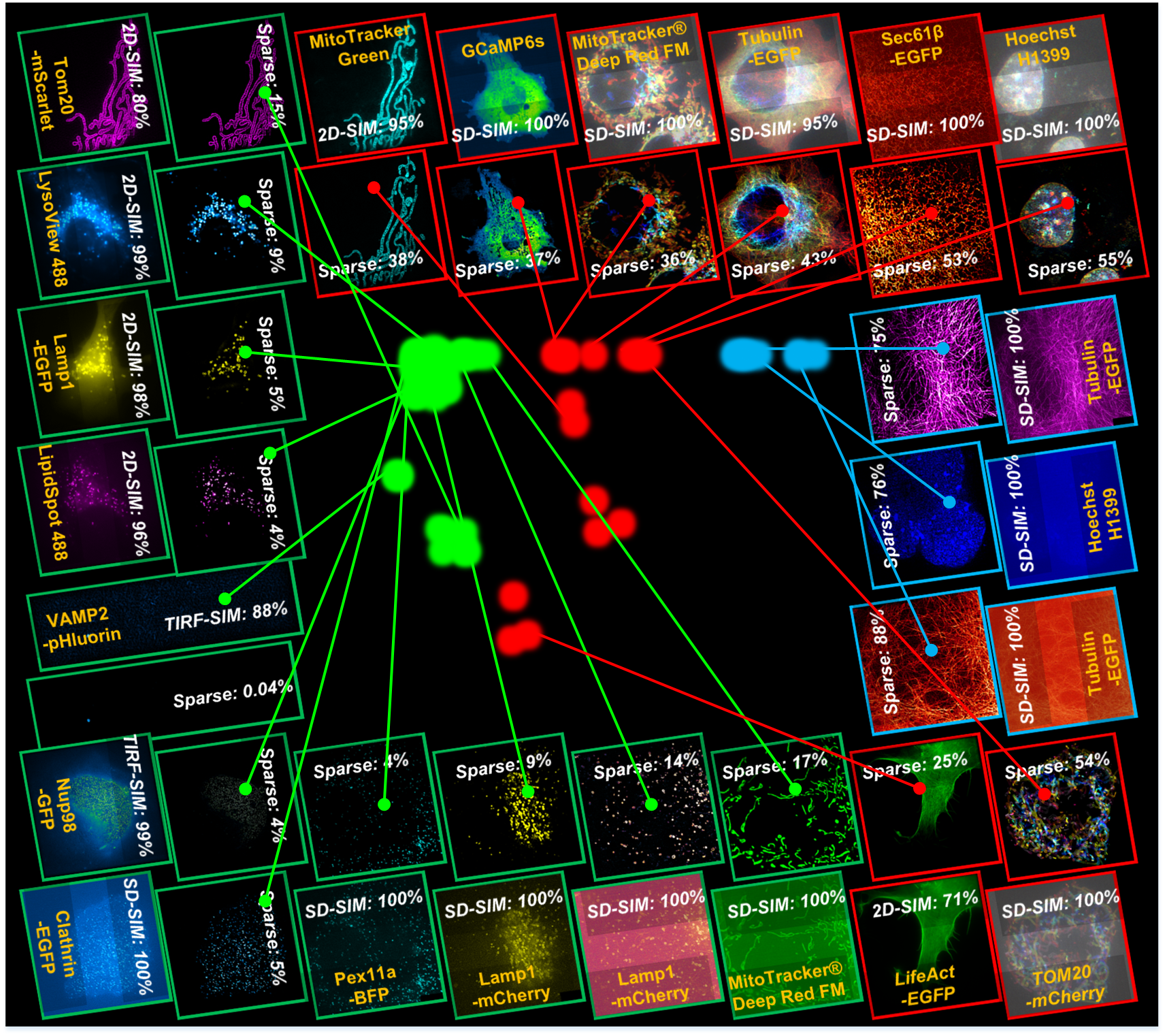
Sparse deconvolution
An universal post-processing framework for fluorescence microscopy. Taking advantage of the prior knowledge of the microscopy PSF-induced sparsity and continuity, we develop a multiconstrained deconvolution algorithm that extends twofold resolution beyond physical limits posed by any existing microscopy hardware under low SNR conditions.
It has been tested on VARIOUS types of:
1. Wide-field microscopy;
2. TIRF microscopy;
3. Light-sheet microscopy;
4. Confocal microscopy;
5. Multi-photon microscopy;
6. Structured illumination microscopy;
7. Fluctuation-based super-resolution microscopy;
8. Expansion microscopy;
9. STED microscopy;
10. Single-molecule localization microscopy for preprocess.
Feasible for single-slice, time-lapse, and volumetric datasets.
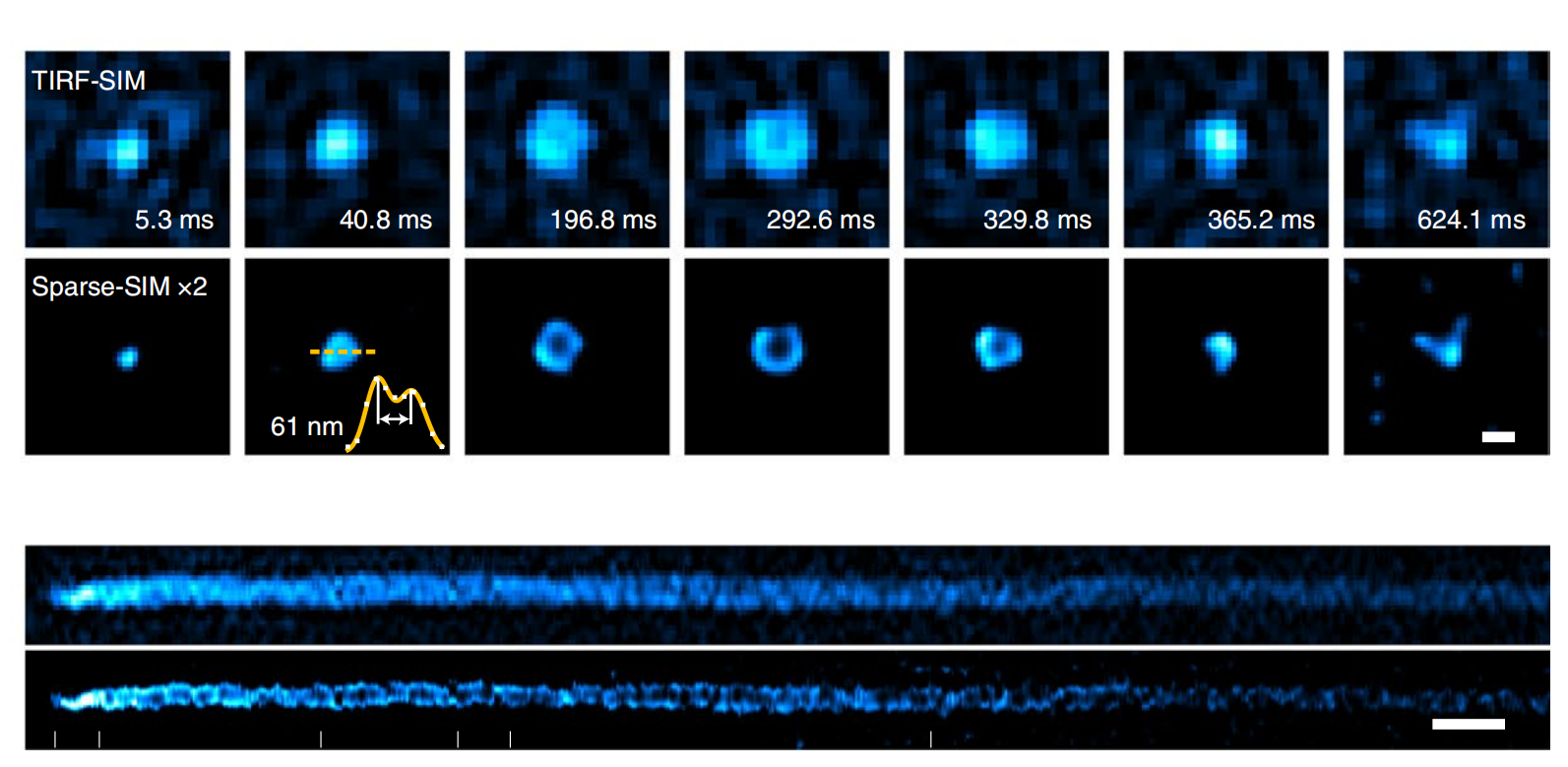
Ultrafast, 60 nm, 564 Hz Sparse-SIM
The Sparse deconvolution assisted structured illumination microscopy (Sparse-SIM) achieves ~60 nm resolution at a temporal resolvability of ~2 ms (~564 Hz), allowing it to resolve intricate structures, including small vesicular fusion pores and relative movements between the inner and outer membranes of mitochondria in live cells.
Paper Code Gallery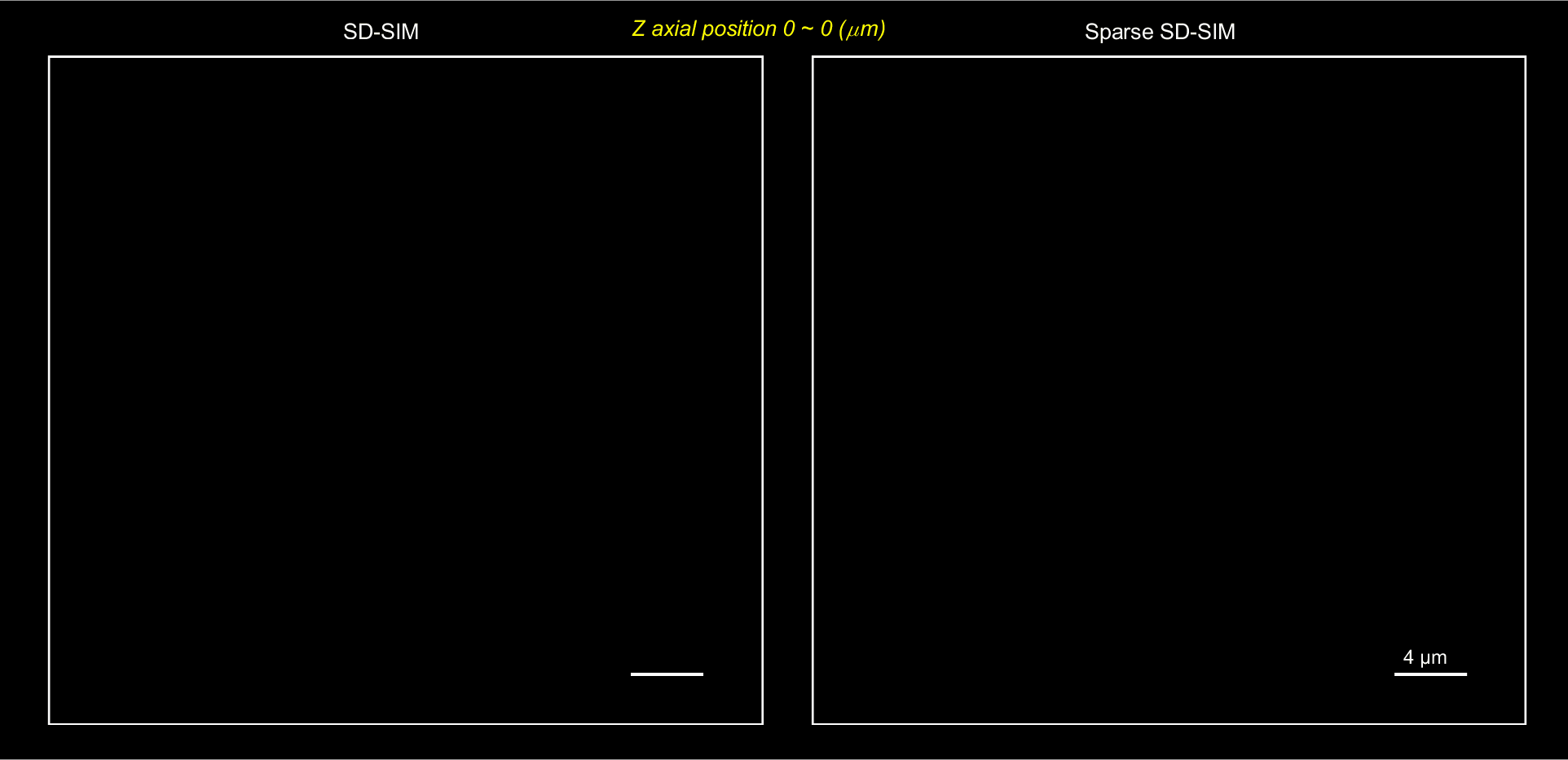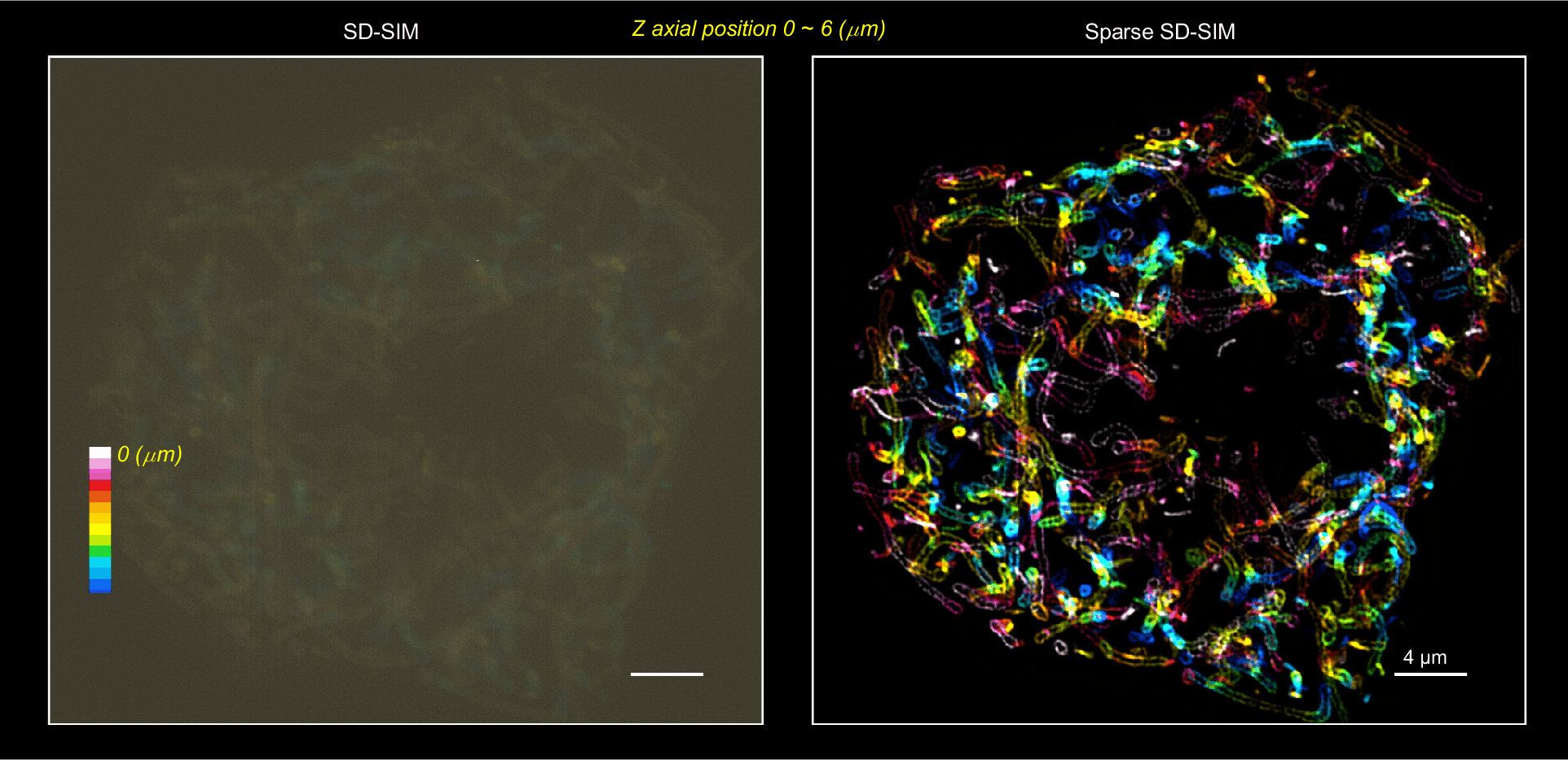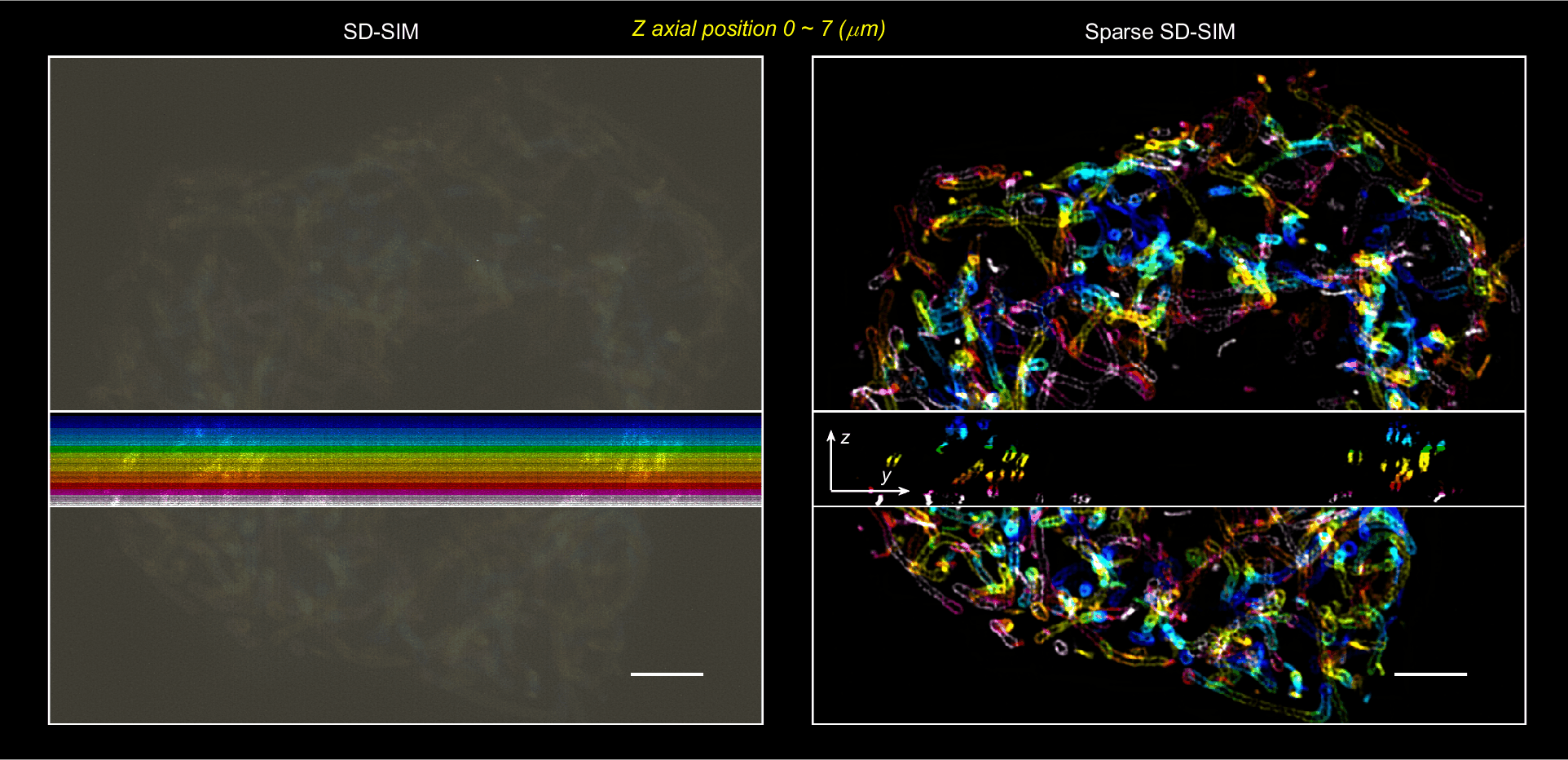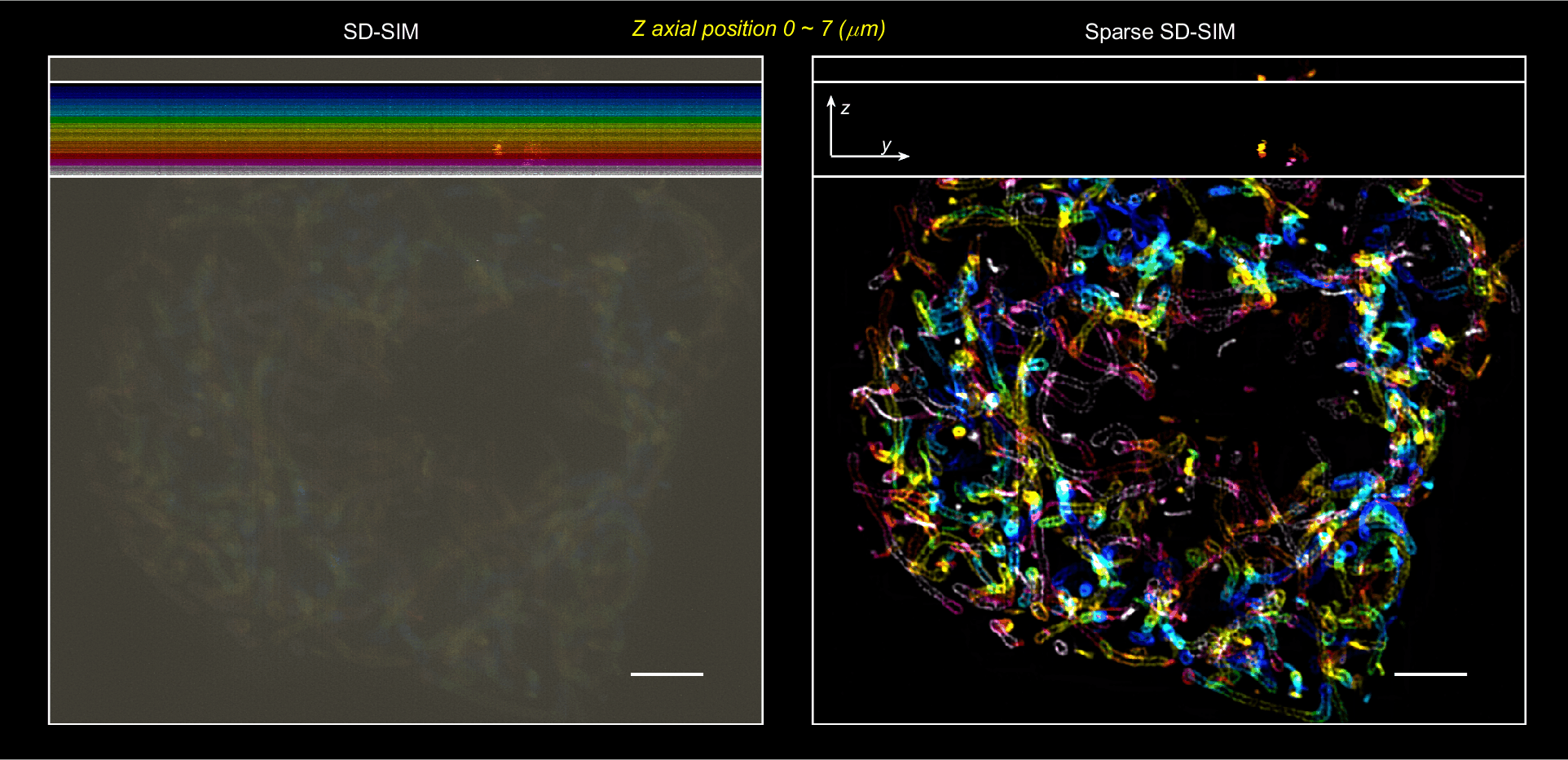
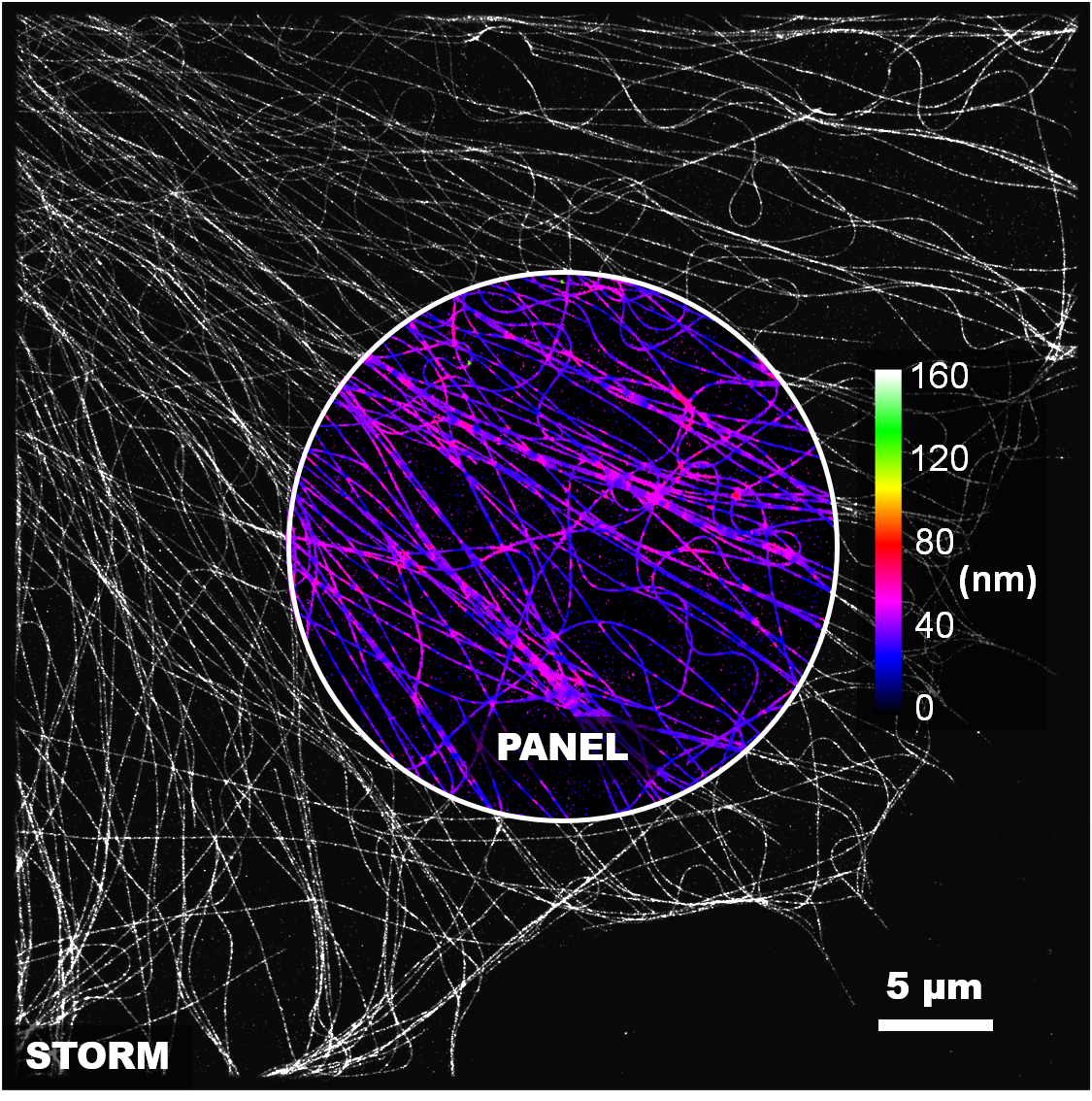
Local image quality mapping
PANEL (pixel-level analysis of error locations) framework for quantitatively mapping reconstruction quality at super-resolution scale (can assess both conventional and deep-learning methods).
rFRC: The rolling Fourier ring correlation (rFRC) is for quantitatively mapping the local image quality (effective resolution, data uncertainty). The lower effective resolution gives a higher probability to the error existence, and thus we can use it to represent the uncertainty revealing the error distribution.
PANEL: We also accompany our filtered rFRC with truncated RSM (resolution-scaled error map) as a full PANEL map, but this RSM is an optional feature that can be turn off as the wide-field reference being unavailable. PANEL is for biologists to qualitatively pinpoint regions with low reliability as a concise visualization.
Fluctuation-based super-resolution
SACD (super-resolution method based on auto-correlation with two-step deconvolution): A faster fluorescence fluctuation-based super resolution reconstruction method needs ~50 times less frames.
1. SACD only needs 20 frames to achieve twofold lateral and axial resolution improvements.
2. SACD requires no additional optical components, and can offer a direct and flexible add-on super-resolution feature on any off-the-shelf commercialized microscopes or in-house customized systems.
3. Sparse deconvolution-assisted SACD (Sparse-SACD) allows fast 4D super-resolution live-cell imaging.
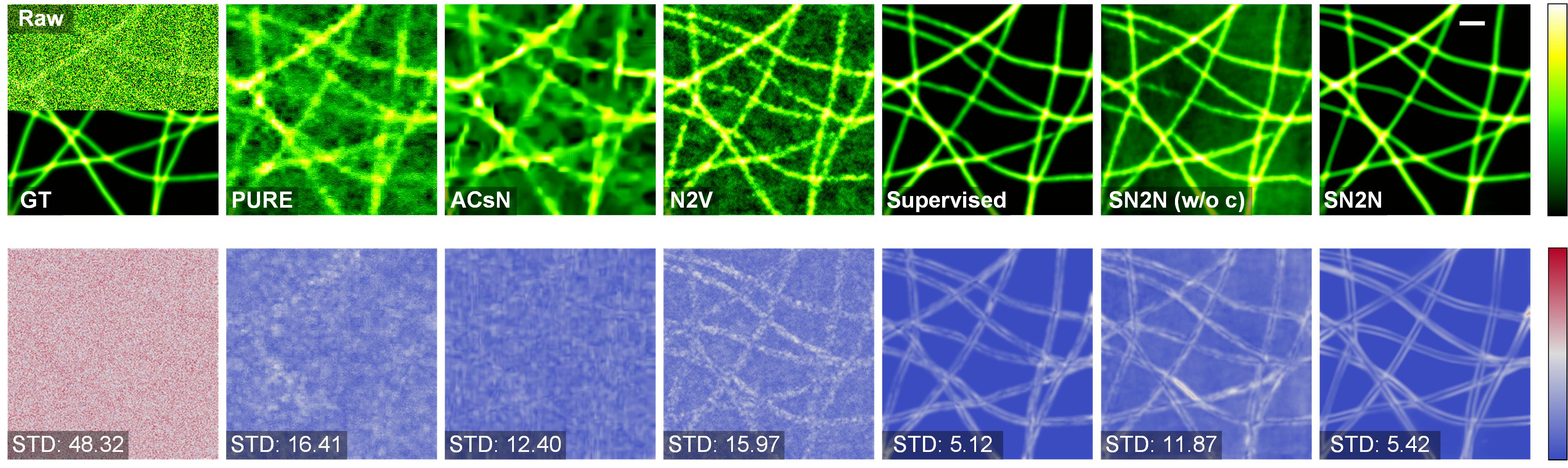
Unsupervised learning to denoise
Every collected photon is precious in live-cell super-resolution (SR) microscopy. Here, we develop a data-efficient deep learning-based denoising solution to improve diverse SR imaging modalities. The method, SN2N, is a Self-inspired Noise2Noise module with self-supervised data generation and self-constrained learning process. SN2N is fully competitive with supervised learning methods and circumvents the need for large training-set and clean ground-truth, requiring only a single noisy frame for training. We show that SN2N improves photon efficiency by one-to-two orders of magnitude and is compatible with multiple imaging modalities for volumetric, multicolor, time-lapse SR microscopy. We further integrated SN2N into different SR reconstruction algorithms to effectively mitigate image artifacts. We anticipate SN2N will enable improved live SR imaging and inspire further advances.
Paper Pre-print Code GalleryBiomedical informatics (imaging-based)
With upgraded imaging platform and smart analysis algorithms, we empower the robust high-throughput bioimage profiling. For instance, using SARS-CoV-2 single virus-like particle (VLP) tracking in live cells and sparse deconvolution algorithm, we uncover that VLPs utilize filopodia to reach the entry site in two patterns, “surfing” and “grabbing”, which avoid the virus from randomly searching on the plasma membrane.
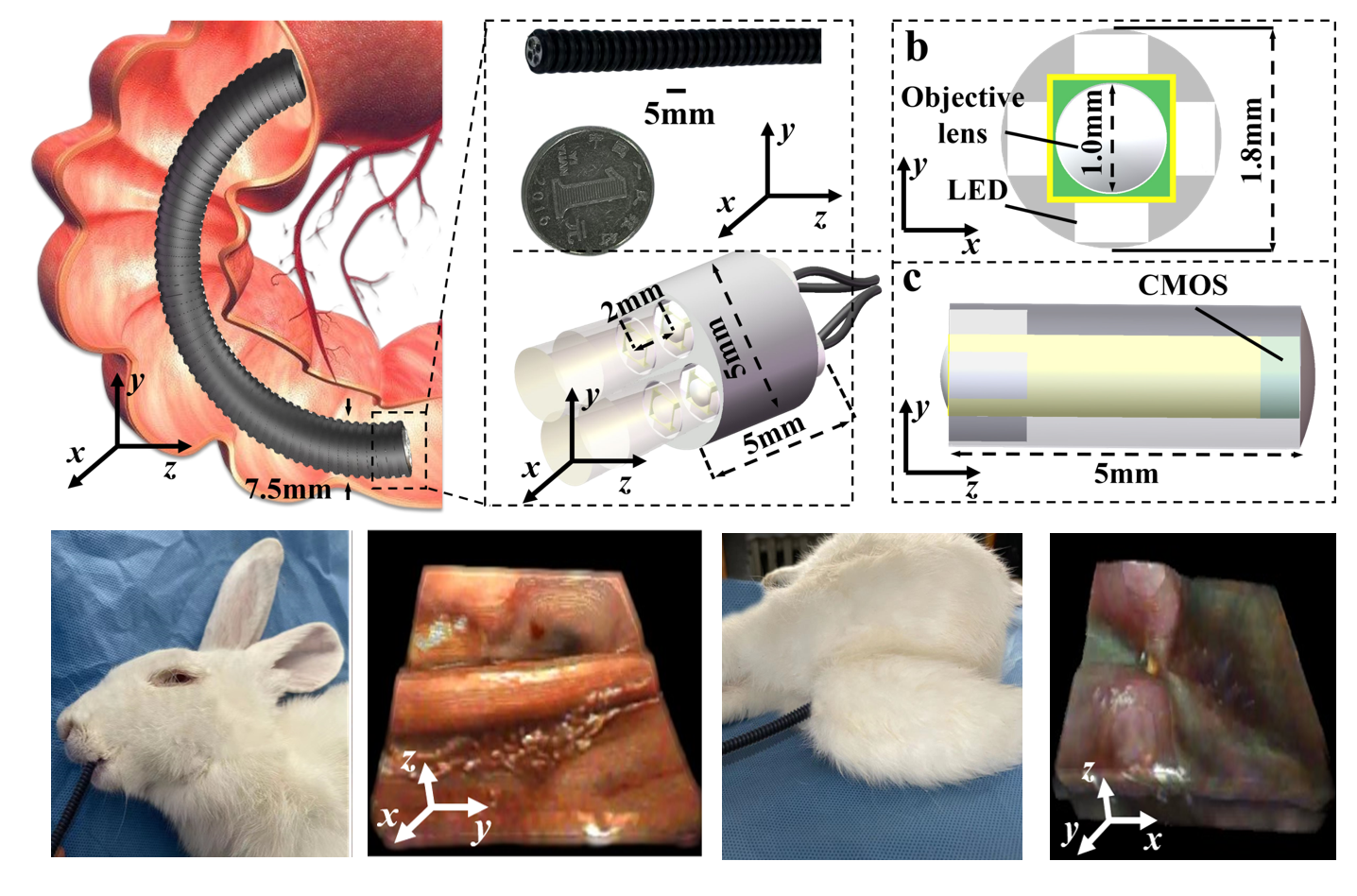
Paper GallerySingle-shot volumetric 5 mm endoscopic probe
We designed a highly flexible, compact, single-shot volumetric, high-resolution endoscopic probe by employing precision-machined multiple micro-imaging devices (MIRDs). To further protect the flexibility, the MIRD with a diameter and height of 5 mm is packaged in pliable polyamide, using soft data cables for data transmission. It achieves the optimal lateral resolvability of 31 µm and axial resolvability of 255 µm, with an imaging volume over 2.3 × 2.3 × 10 mm3. Our technique allows easy access to the organism interior through the natural entrance, which has been verified through observational experiments of the stomach and rectum of a rabbit.
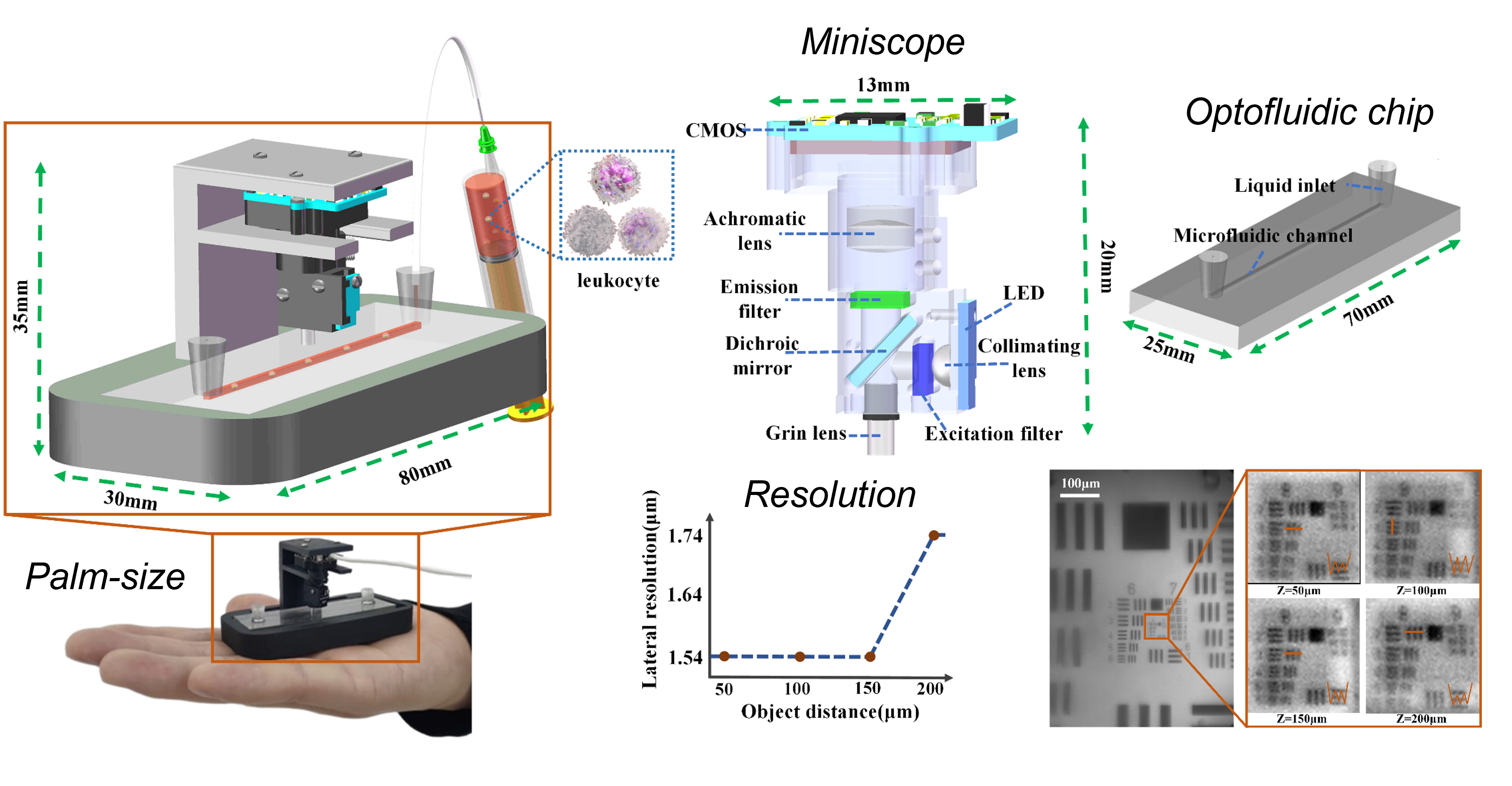
Paper GallerySmart palm-size optofluidic hematology analyzer
We devised a smart Palm-size Optofluidic Hematology Analyzer based on a miniature fluorescence microscope and a microfluidic platform to lighten the device to improve its portability. This gadget has a dimension of 35 × 30 × 80 mm and a mass of 39 g, less than 5% of the weight of commercially available flow cytometers. Additionally, automatic leukocyte concentration detection has been realized through the integration of image processing and leukocyte counting algorithms.
Paper Gallery